

Francisco J. Terán obtained his PhD in Physics (November 2001) at Université Joseph Fourier in Grenoble (France) under supervision of Prof. Marek Potemski. Then, Dr. Teran realized different postdoctoral stays at the Quantum Transport group at the University of Nothingham working with Prof. Laurence Eaves, back to Grenoble High Magnetic Field Lab CNRS-MPI/FKF, SemicUAM group at the Universidad Autónoma de Madrid working with Prof. José Manuel Calleja (Juan de la Cierva fellow). On March 2007, Dr. Teran joined IK4-Gaiker Technological Center as Senior researcher (2008 Torres Quevedo fellowship). On April 2009, Dr. Terán joined IMDEA Nanociencia (2012-2017 as a Ramón y Cajal fellowship) to strength the research line on magnetic nanoparticles for biomedical applications. From 2010 to 2013, Dr. Teran led the AFM Service. Since 2012, Dr. Teran is leading the Hyperthermia Lab and since 2014 the Advanced Instrumentation Service.
The study of the influence of intrinsic (size, chemical composition) and extrinsic (biological matrix, field conditions, aggregation, concentration, viscosity, etc..) parameters on the AC magnetic response (including magnetic heating) of magnetic nanoparticles.
The study of the influence of biological matrices and fluids on the AC magnetic response of magnetic nanoparticles.
The use of magnetic nanoparticles as magnetic transducer for sensing molecular markers in biological fluids.
Heating losses of iron oxide nanoparticles activated by magnetic or optical means physical mechanisms related to photothermal response of magnetic nanoparticles.
The development and validation of instrumentation for advanced magnetic measurements (https://sites.google.com/site/servinsimdeanano/home).
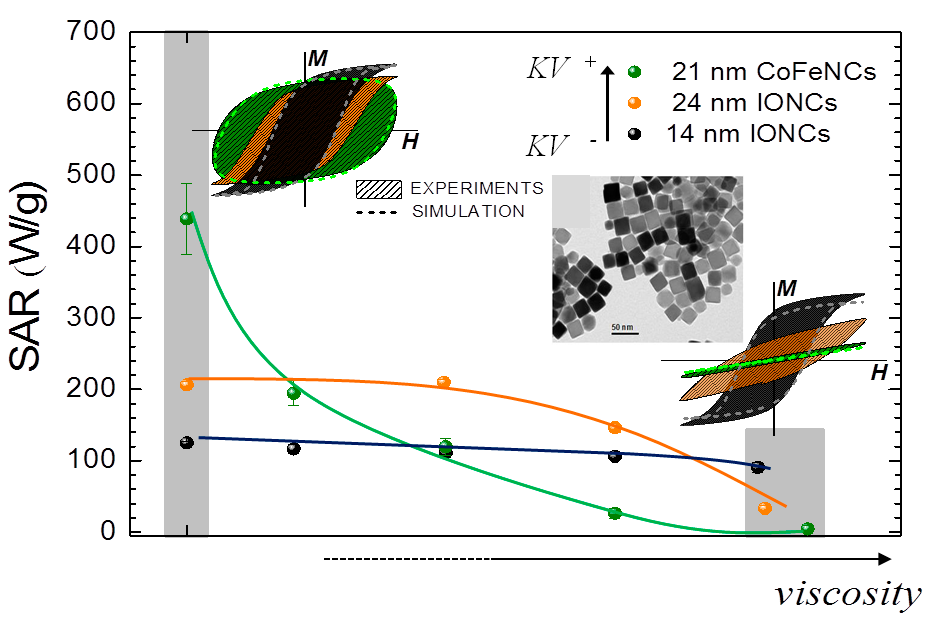
· "Unraveling viscosity effects on the hysteresis losses of magnetic nanocubes" D. Cabrera, A. Lak, T. Yoshida, M.E. Materia, D. Ortega, F. Ludwig, P. Guardia, A. Sathya, T. Pellegrino, and F. J. Teran. Nanoscale 9, 5094 (2017).
· "Elucidation of the physico-chemical properties ruling the colloidal stability of iron oxide nanoparticles under physiological conditions"A. Aires, D. Cabrera, L. C. Alonso-Pardo, A. L. Cortajarena and F. J. Teran. Chem.Nano.Mat.3,183 (2017). Front Cover.
· "Nanoparticle-based hyperthermia distinctly impacts ROS production, Ki-67, TOP2A, TPX2- expression and apoptosis induction in pancreatic cancer" R. Ludwig, F.J.Teran, U. Teichgraeber, and I. Hilger.Int.J. Nanomedicine 12, 1009 (2017).
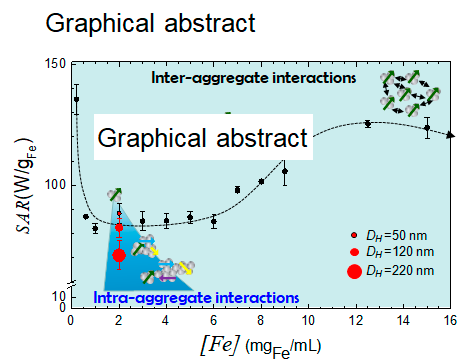
· " Effects of inter- and intra-aggregate magnetic dipolar interactions on the magnetic heating efficiency of iron oxide nanoparticles" J. G. Ovejero, D. Cabrera, J. Carrey, T. Valdivielso, G. Salas and F. J. Teran. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 18, 10954 (2016).
· “Controlled synthesis of uniform magnetite nanocrystals with high-quality properties for biomedical applications” G. Salas, et al. J. Mater.Chem. 22, 21065 (2012).
· "Unraveling viscosity effects on the hysteresis losses of magnetic nanocubes" D. Cabrera, A. Lak, T. Yoshida, M.E. Materia, D. Ortega, F. Ludwig, P. Guardia, A. Sathya, T. Pellegrino, and F. J. Teran. Nanoscale 9, 5094 (2017).
· "Elucidation of the physico-chemical properties ruling the colloidal stability of iron oxide nanoparticles under physiological conditions"A. Aires, D. Cabrera, L. C. Alonso-Pardo, A. L. Cortajarena and F. J. Teran. Chem.Nano.Mat.3,183 (2017). Front Cover.
· "Nanoparticle-based hyperthermia distinctly impacts ROS production, Ki-67, TOP2A, TPX2- expression and apoptosis induction in pancreatic cancer" R. Ludwig, F.J.Teran, U. Teichgraeber, and I. Hilger.Int.J. Nanomedicine 12, 1009 (2017).
· " Effects of inter- and intra-aggregate magnetic dipolar interactions on the magnetic heating efficiency of iron oxide nanoparticles" J. G. Ovejero, D. Cabrera, J. Carrey, T. Valdivielso, G. Salas and F. J. Teran. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 18, 10954 (2016).
· “Controlled synthesis of uniform magnetite nanocrystals with high-quality properties for biomedical applications” G. Salas, et al. J. Mater.Chem. 22, 21065 (2012).
 |
 |
 |